Are you ready to build your own accounting software using Java? Imagine having a tool tailored exactly to your needs—simple, reliable, and powerful enough to manage your finances effortlessly.
This guide will walk you through every step to create software that keeps your accounts organized and your business running smoothly. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to develop a system that saves you time and money. Keep reading, and let’s turn your idea into a working Java application you can be proud of.
Setting Up Your Java Environment
Setting up your Java environment is the first step in creating accounting software. A proper setup ensures smooth coding and fewer errors. It involves installing necessary tools and organizing your project files correctly. These tasks help you focus on writing clean, efficient code.
Installing Jdk And Ide
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is essential for writing Java programs. Download the latest JDK version from the official Oracle website. Follow the installation instructions for your operating system. After installing JDK, choose an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse. IDEs simplify coding with features like auto-completion and debugging tools.
Configuring Project Structure
Create a new project in your IDE after installation. Organize your files into folders like src for source code and lib for external libraries. Set up a clear package structure to keep related classes together. Proper structure makes your code easier to read and maintain. It also helps in managing large projects efficiently.

Credit: developer.intuit.com
Designing The Software Architecture
Designing the software architecture is a key step in creating accounting software in Java. A clear structure helps the program run smoothly and stay easy to update. Good architecture breaks the software into parts that work well together. This makes coding faster and reduces errors. It also helps in managing the complex tasks of accounting. Let’s explore how to design this architecture efficiently.
Choosing Design Patterns
Design patterns solve common software problems. They provide tested solutions that save time. For accounting software, use patterns like Model-View-Controller (MVC). MVC separates data, user interface, and control logic. This keeps the code clean and easy to change. Another useful pattern is Singleton. It ensures only one instance of important classes, like database connections. Using these patterns creates a strong base for your software.
Planning Modules And Components
Divide the software into modules to manage tasks clearly. Common modules include User Management, Invoice Processing, and Reporting. Each module handles a specific part of the accounting process. Components inside modules work together for the module’s task. This approach helps find and fix problems quickly. It also allows adding new features without breaking existing ones. Plan each module with clear roles and simple connections.
Creating The User Interface
Creating the user interface is a key step in building accounting software in Java. The interface lets users interact with the software easily. A clear and simple design helps users complete tasks fast. Good UI design also reduces errors and improves user satisfaction.
Careful planning of the UI makes the software more effective. It should show all important information without clutter. Controls like buttons, text fields, and menus must be easy to find and use. The interface must also work well on different screen sizes.
Selecting Ui Frameworks
Choosing the right UI framework affects development speed and software quality. Java offers several options for building interfaces. Swing is an older, stable choice with many components. JavaFX is newer, with modern controls and better graphics.
JavaFX supports responsive design and multimedia features. It works well for complex layouts and animations. Swing is easier for simple forms and classic desktop apps. Consider your project size and needs before selecting a framework.
Designing Forms And Layouts
Forms collect user input like invoices, payments, and reports. Keep forms simple and organized. Group related fields together. Use labels to explain each input clearly.
Use layout managers to arrange components neatly. Grid layout and border layout are popular choices in Java. Ensure enough space between fields. Make buttons like “Save” and “Cancel” easy to find.
Test the forms to confirm they are user-friendly. Adjust the design based on feedback. Good form design speeds up data entry and reduces mistakes.
Implementing Core Accounting Features
Implementing core accounting features is the heart of any accounting software. This step ensures the software can handle essential financial tasks accurately. It helps users manage their money, track expenses, and view reports easily.
Building these features in Java requires careful planning and clear code structure. Each function must work smoothly and without errors. Let’s explore the key components needed for a basic accounting system.
Managing Accounts And Ledgers
Accounts and ledgers store financial data. Create classes to represent different account types. Use methods to add, update, or delete accounts. Organize accounts into categories such as assets, liabilities, and equity. This organization helps in tracking money flow clearly.
Ledgers record all financial activities. Implement ledger entries that link to accounts. Maintain a balance for each account by updating ledger entries. This helps keep data accurate and consistent.
Recording Transactions
Transactions are the core actions in accounting. Design a transaction class with details like date, amount, and description. Each transaction affects at least two accounts. Use double-entry bookkeeping to keep balances correct.
Write functions to add new transactions and validate data. Ensure transactions update the related accounts and ledgers immediately. This process keeps financial records up to date and reliable.
Generating Financial Reports
Reports summarize financial data for users. Build modules to generate key reports like balance sheets and income statements. These reports pull data from accounts and ledgers.
Format reports clearly for easy reading. Include totals and subtotals to show financial health. Regular reports help users understand their finances better and make informed decisions.
Integrating Database Support
Integrating database support is essential for building accounting software in Java. It stores financial data safely and allows easy access. Proper database integration ensures your software runs smoothly and handles data efficiently.
Choosing the right database and connecting it to Java is the next step. You also need to perform CRUD operations to manage data. These tasks help create a functional and reliable accounting application.
Choosing A Database
Select a database based on your software needs. Common choices include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite. MySQL and PostgreSQL work well for large data and multi-user access. SQLite is simpler and good for smaller projects. Consider speed, scalability, and ease of use.
Connecting Java With Database
Use JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) to link Java with your database. JDBC acts as a bridge between Java code and the database. Load the database driver in your code first. Then create a connection using the database URL, username, and password. Always handle exceptions to avoid crashes.
Performing Crud Operations
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete. These operations manage data in your accounting software. Use SQL queries within Java to perform each action. For example, INSERT adds new records, SELECT fetches data, UPDATE changes existing entries, and DELETE removes data. Test each operation carefully to ensure accuracy.
Adding Security Measures
Adding security measures is crucial in accounting software development. It protects sensitive financial data from unauthorized access. Security builds trust with users and helps comply with laws.
Strong security reduces risks of data breaches. Focus on user authentication and data encryption. These two steps create a safer environment for your software.
Implementing User Authentication
User authentication controls who can access the software. Require users to log in with a username and password. Store passwords securely using hashing algorithms like bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Consider adding multi-factor authentication for extra protection. This means users enter a code sent to their phone or email. Limit login attempts to prevent brute force attacks.
Encrypting Sensitive Data
Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Use SSL/TLS protocols to secure data sent over the internet. Encrypt stored data using strong algorithms such as AES.
Encryption ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable. Manage encryption keys carefully and restrict access to them. Regularly update your encryption methods to stay ahead of threats.
Testing And Debugging
Testing and debugging are crucial steps in creating accounting software in Java. They ensure your program works correctly and handles data safely. Without testing, errors may go unnoticed and cause problems later. Debugging helps find and fix these errors quickly. Both steps improve the software’s quality and user trust.
Writing Unit Tests
Unit tests check small parts of your code separately. Write tests for each function to confirm it returns the right results. Use frameworks like JUnit to automate these tests. Run tests often to catch errors early. This saves time and effort during development.
Handling Exceptions
Exceptions happen when the program faces unexpected situations. Handle exceptions using try-catch blocks to keep the program running. Show clear error messages to users. Log errors for future analysis. Proper exception handling prevents crashes and data loss.
Debugging Common Issues
Debugging helps find bugs in your code. Use tools like Eclipse or IntelliJ to step through code line by line. Check variable values and program flow carefully. Common issues include incorrect calculations and data input errors. Fix these by reviewing logic and validating inputs.
Credit: stratoflow.com
Packaging And Deployment
Packing and deploying your Java accounting software is a key step. It lets users run your program easily. You create a package that contains all code and resources. Then, you share this package so others can use your software.
This process also helps keep your software organized. It makes updates simpler. Proper packaging improves performance and reliability.
Building Executable Jar
Create an executable JAR file to bundle your Java classes and resources. This file acts like a standalone app. Users can run it with a simple command.
Use the Java compiler to compile your code first. Then, use the jar tool to package everything. Include a manifest file with the entry point class name. This tells Java which class to run first.
Example command:
jar cfe AccountingApp.jar MainClass .class resources/This command builds AccountingApp.jar with MainClass as the start. Make sure to test the JAR on your computer before sharing.
Deploying On Different Platforms
Java software runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Packaging as a JAR makes your program cross-platform. Users only need Java Runtime Environment installed.
For Windows, create a batch file to run the JAR easily. For macOS and Linux, use shell scripts. These scripts help users start the app without typing full commands.
Consider bundling a Java runtime with your app. This avoids version conflicts on user machines. Tools like jlink help create custom runtimes.
Test your software on each platform before release. Check for any platform-specific issues or errors.
Enhancing With Advanced Features
Enhancing your Java accounting software with advanced features improves its usability and reliability. These features allow multiple users to access the system securely. Cloud storage integration helps keep data safe and accessible from anywhere. Automating backups ensures no data is lost, adding peace of mind.
Adding Multi-user Support
Multi-user support lets several people use the software at the same time. This is useful for teams working on the same accounts. Implement user roles to control access to sensitive data. Use Java’s concurrency tools to manage multiple sessions smoothly. This makes the software more flexible and efficient.
Integrating Cloud Storage
Cloud storage keeps your data safe outside the local system. Use cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure for storage. Java libraries simplify connecting to these services. Cloud storage allows users to access data from any device. It also helps with data recovery after hardware failure.
Automating Backups
Automated backups save your data regularly without manual effort. Schedule backup tasks using Java’s Timer or ScheduledExecutorService. Store backups in a secure location, like cloud or external drives. Automated backups reduce the risk of data loss. They keep your accounting records safe and up to date.
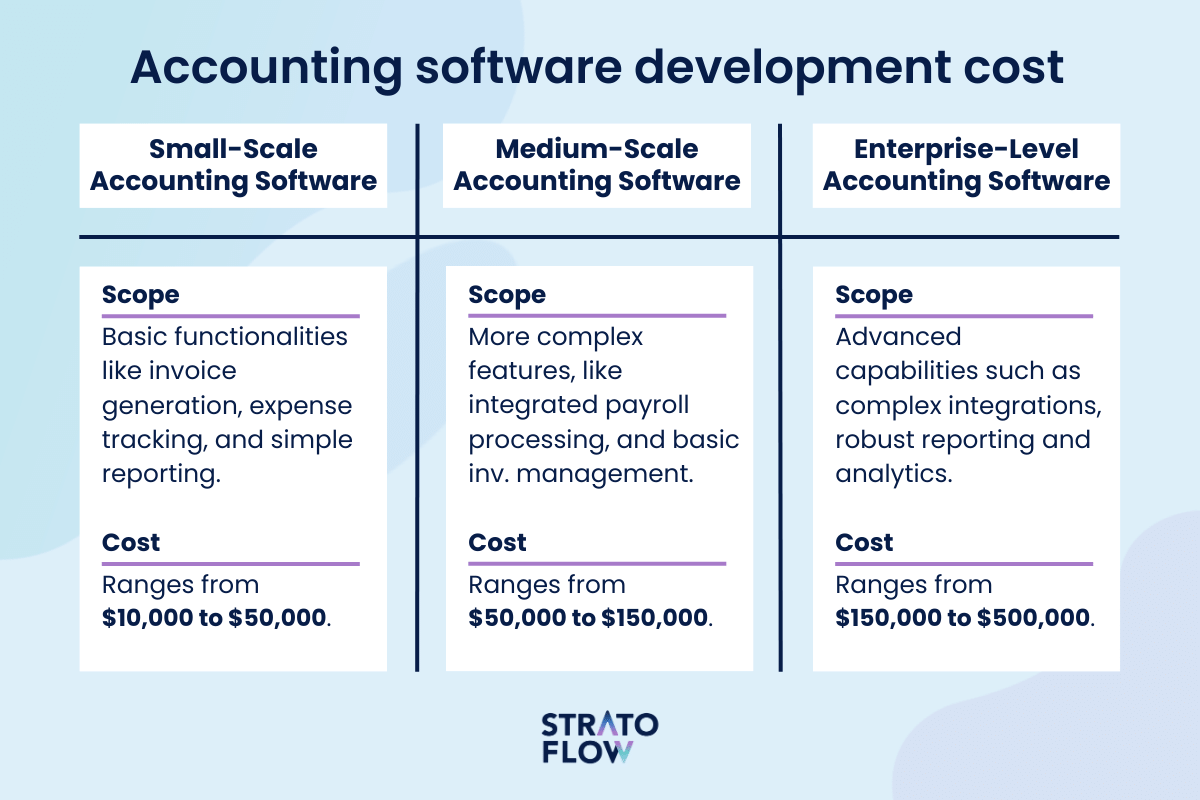
Credit: stratoflow.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Basic Features Of Java Accounting Software?
Java accounting software typically includes invoicing, expense tracking, financial reporting, and ledger management. These features help businesses monitor finances efficiently. Java’s robustness ensures secure and scalable accounting solutions suitable for various business sizes.
How Do I Start Coding Accounting Software In Java?
Begin by outlining core modules like transactions, accounts, and reports. Use Java frameworks such as Spring for backend development. Focus on database integration with MySQL or PostgreSQL to store financial data securely and efficiently.
Which Java Libraries Aid Accounting Software Development?
Libraries like Apache POI help generate Excel reports, while JFreeChart supports creating financial charts. Hibernate simplifies database operations. These tools speed up development and enhance software functionality.
How To Ensure Data Security In Java Accounting Software?
Implement encryption for sensitive data and use secure authentication methods. Regularly update dependencies and follow Java security best practices to protect financial information from breaches.
Conclusion
Creating accounting software in Java takes time and effort. Start with simple features like recording transactions. Build step by step, testing each part carefully. Use clear code and organize it well. Keep the user’s needs in mind always. This helps create software that is easy to use.
Practice coding regularly to improve your skills. Soon, you will have a working accounting tool. Stay patient and keep learning along the way. This journey will teach valuable programming lessons.







