Are you looking for a simple way to manage your finances without buying expensive software? Creating your own accounting software in Excel can be the perfect solution.
Imagine having a tool tailored exactly to your needs, helping you track income, expenses, and profits all in one place. In this guide, you’ll discover easy steps to build a powerful accounting system using Excel, even if you’re not a tech expert.
Keep reading, and you’ll soon have a custom tool that saves you time and keeps your finances organized like never before.
Credit: quickbooks.intuit.com
Planning Your Accounting Software
Planning is the first step in creating accounting software in Excel. It helps set a clear path for your project. A good plan saves time and avoids confusion later. You need to think about what your software should do. Also, decide how users will interact with it. Organizing your data structure is essential too. This section guides you through these important planning stages.
Identifying Key Features
Start by listing the main tasks your software must perform. Common features include tracking income and expenses. You may want to add invoicing and payment tracking. Budget creation and financial reporting are helpful too. Choose features that match your business needs. Keep the list small at first. You can add more features later.
Designing User Interface
Your software should be easy to use. Design simple menus and buttons. Use clear labels for each section. Keep the layout clean to avoid confusion. Use colors to separate different areas. Make sure users can navigate without help. Test the interface with real users if possible. Their feedback will help improve usability.
Setting Up Data Structure
Organize your data in clear, separate tables. Have one table for transactions and another for accounts. Use columns for dates, amounts, and descriptions. Create unique IDs for each entry. This helps avoid errors and confusion. Plan how tables will link to each other. A good structure makes calculations easier and faster.
Setting Up Excel Workbook
Setting up your Excel workbook correctly is the first step to building effective accounting software. A well-organized workbook makes data entry and analysis easier. It helps prevent mistakes and saves time.
This section covers how to create worksheets, name and organize sheets, and format cells for smooth data entry. Each step builds a solid foundation for your accounting software.
Creating Worksheets
Start by adding multiple worksheets in your Excel file. Each worksheet should serve a clear purpose, like tracking expenses, income, or invoices. Use the “+” button at the bottom to add new sheets. Keep the number of sheets manageable to avoid confusion.
Naming And Organizing Sheets
Give each sheet a simple, descriptive name. For example, use names like “Expenses,” “Income,” and “Summary.” This helps you find information quickly. Arrange sheets in a logical order, such as putting data entry sheets first and summary sheets last.
Formatting Cells For Data Entry
Format cells to match the type of data you will enter. Use number format for amounts, date format for transaction dates, and text format for descriptions. Set column widths to fit data clearly. Use borders and shading to separate sections visually. This makes the workbook easier to read and use daily.
Building The Data Input Forms
Building data input forms is a key step in creating accounting software in Excel. These forms collect and organize user data efficiently. Well-designed forms reduce errors and save time. They make the whole process smooth and clear.
Excel has useful features that help build strong input forms. You can control what users enter and keep data consistent. This section explains how to use Excel tables, data validation, and drop-down lists.
Using Excel Tables
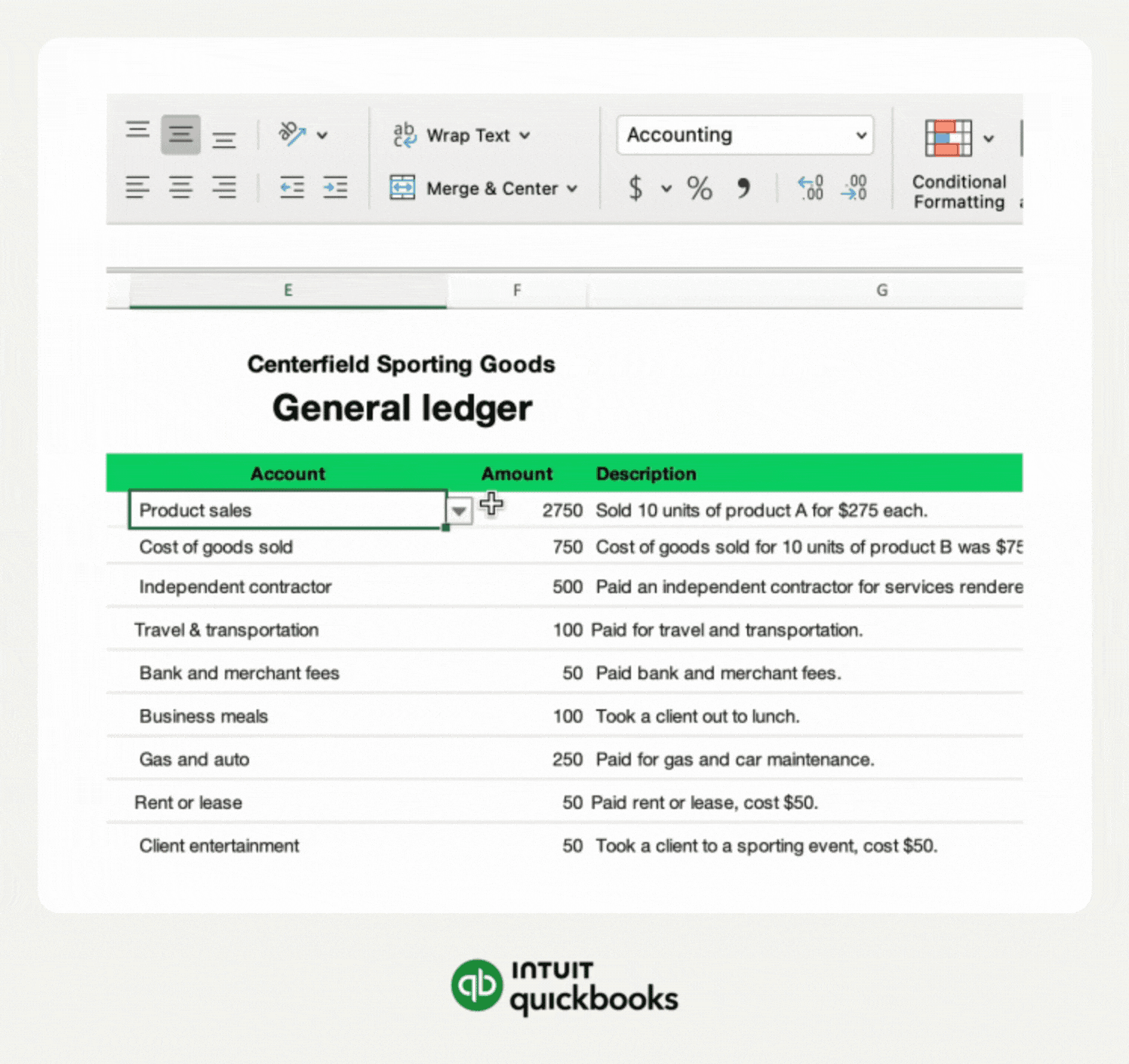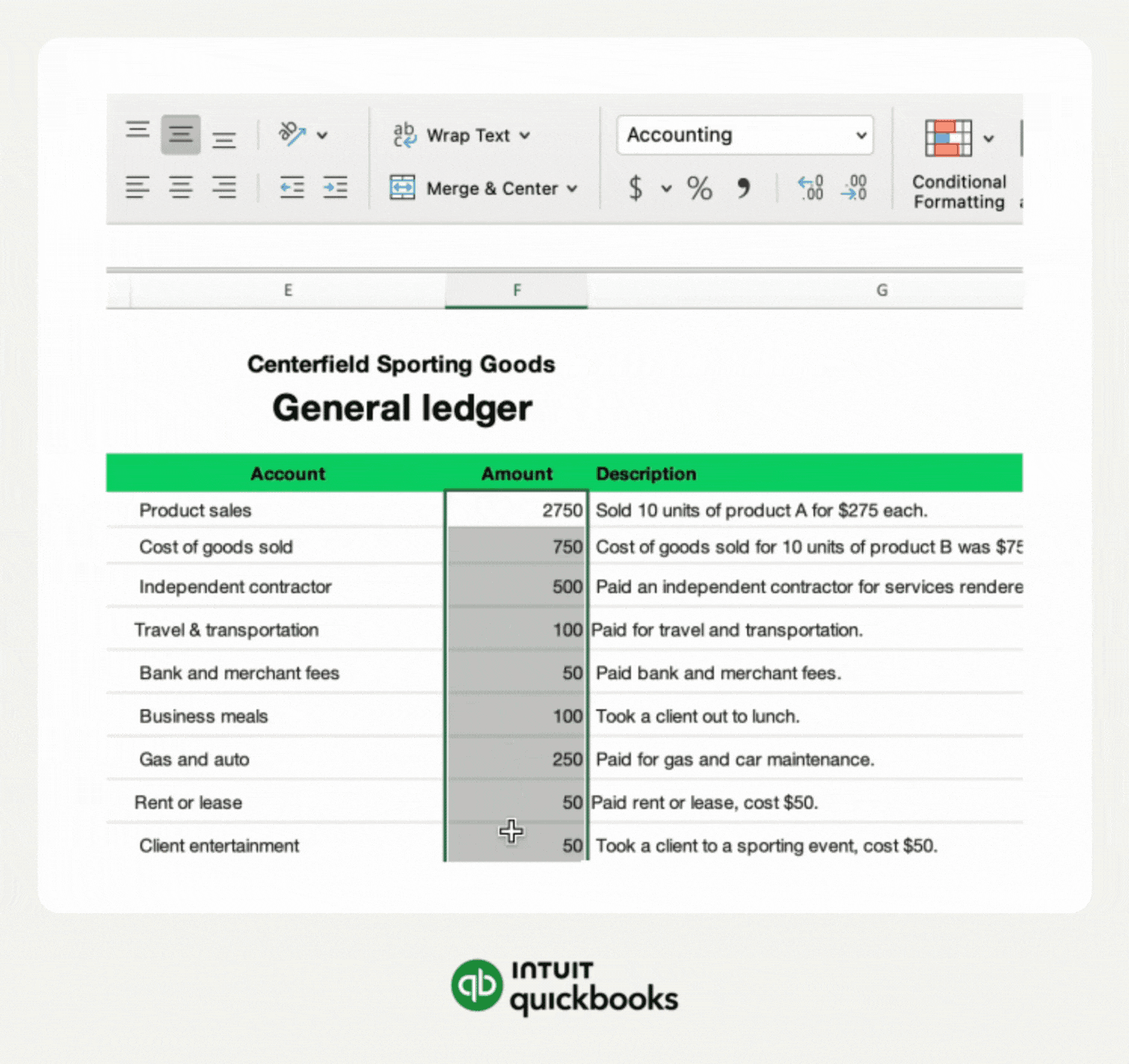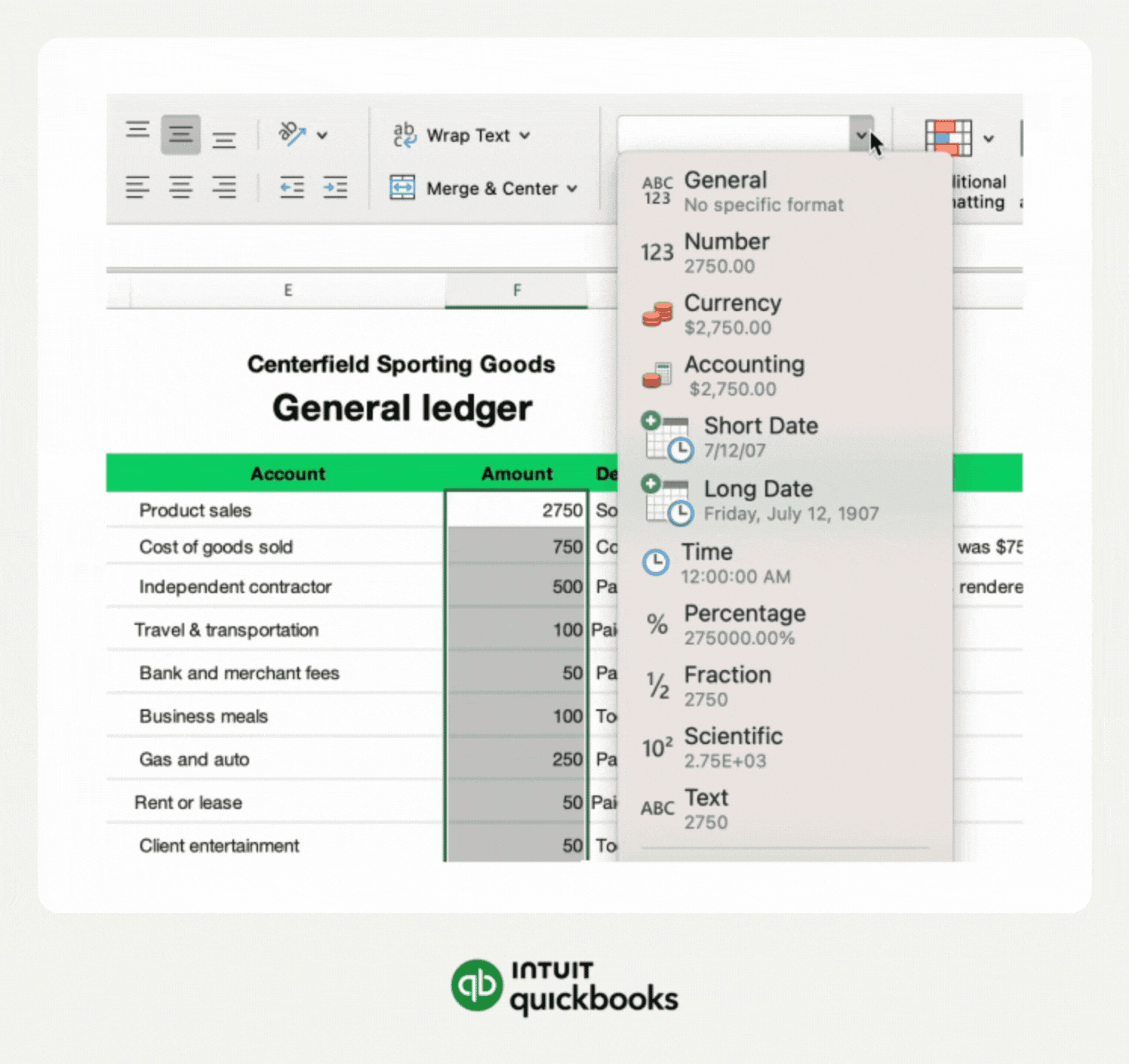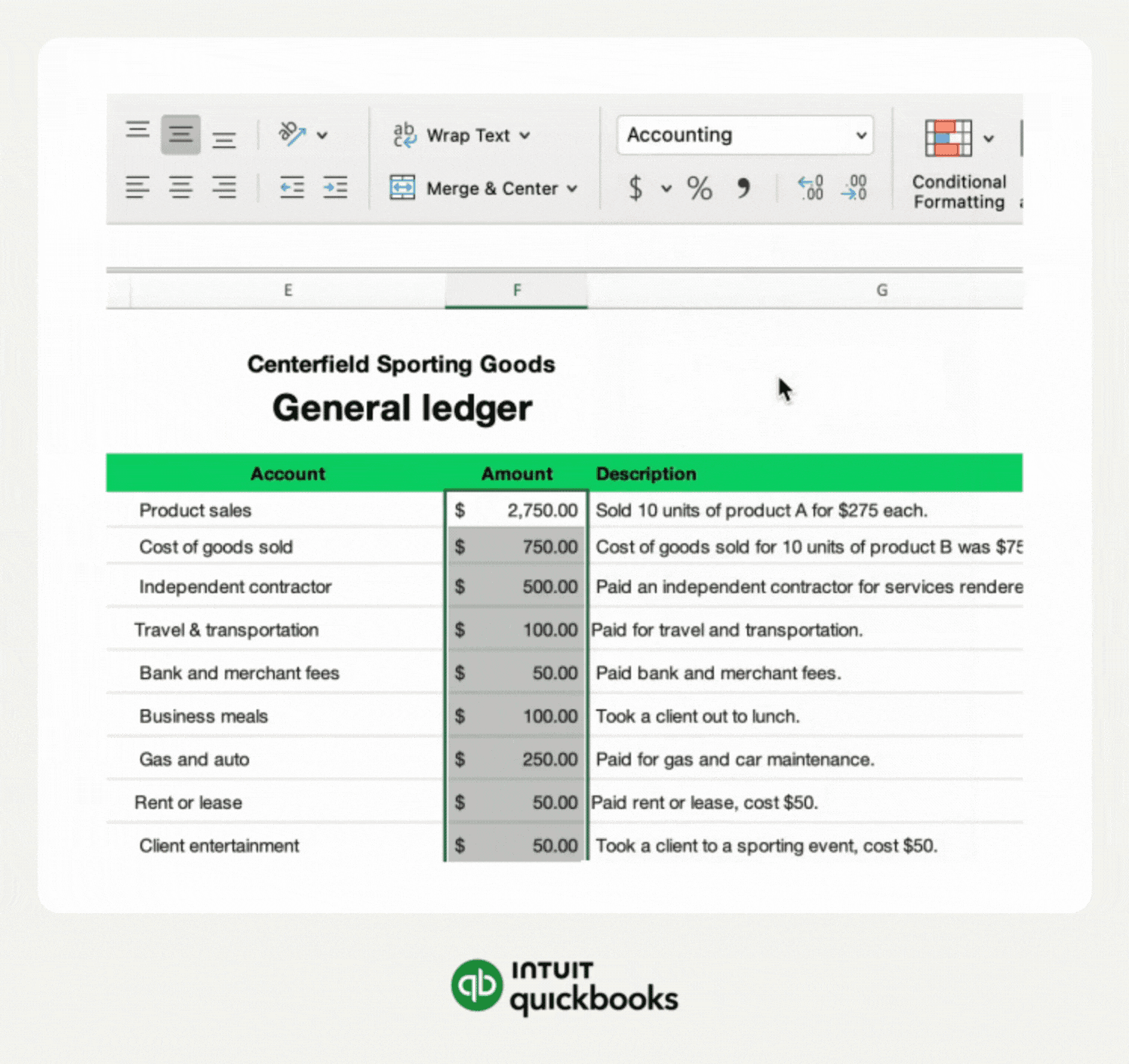
Excel tables organize data into rows and columns. They make managing data easier and more flexible. Tables automatically expand when you add new data. This keeps your input form neat and tidy.
Tables also allow easy sorting and filtering. This helps find information quickly. Use tables as the base for your input forms to keep data structured.
Applying Data Validation
Data validation controls what users can enter in cells. It stops wrong or unwanted data from being added. For example, you can allow only numbers or dates.
Set rules to ensure data is accurate and consistent. This reduces mistakes and keeps your accounting records reliable. Data validation is simple but very powerful.
Creating Drop-down Lists
Drop-down lists let users pick from preset options. This speeds up data entry and lowers errors. Use lists for categories, payment methods, or account types.
Drop-downs guide users to enter valid data. They make your form user-friendly and professional. Creating them is easy with Excel’s data validation feature.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Implementing Formulas And Functions
Implementing formulas and functions is key to making your accounting software in Excel work well. These tools help you perform calculations automatically. They save time and reduce errors. You can create clear, organized financial sheets that update themselves as you add new data. Understanding some basic formulas makes your software smart and efficient.
Calculating Totals And Subtotals
Totals and subtotals give you quick views of your financial data. Use the SUM function to add numbers in a range of cells. It adds values like sales or expenses fast. For subtotals, you can sum smaller groups within your data. This breaks down totals by category or date. Highlight the cells you want, then enter =SUM(start_cell:end_cell). Excel calculates the result instantly.
Using If And Sumif Functions
The IF function checks conditions and returns values based on true or false results. Use it to flag errors or categorize data. For example, mark expenses above a limit. The SUMIF function adds numbers only if they meet a condition. This helps total specific types of transactions. Write =IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false) or =SUMIF(range, criteria, sum_range) to apply these functions.
Automating Date And Time Stamps
Dates and times track when transactions happen. Use the TODAY() function to insert the current date. It updates each day automatically. For exact timestamps, use
Creating Financial Statements
Creating financial statements in Excel helps you track your business health. These statements show profits, assets, and cash flow clearly. Excel allows you to build each statement step-by-step. You can customize the layout and formulas to fit your needs.
Designing Income Statement
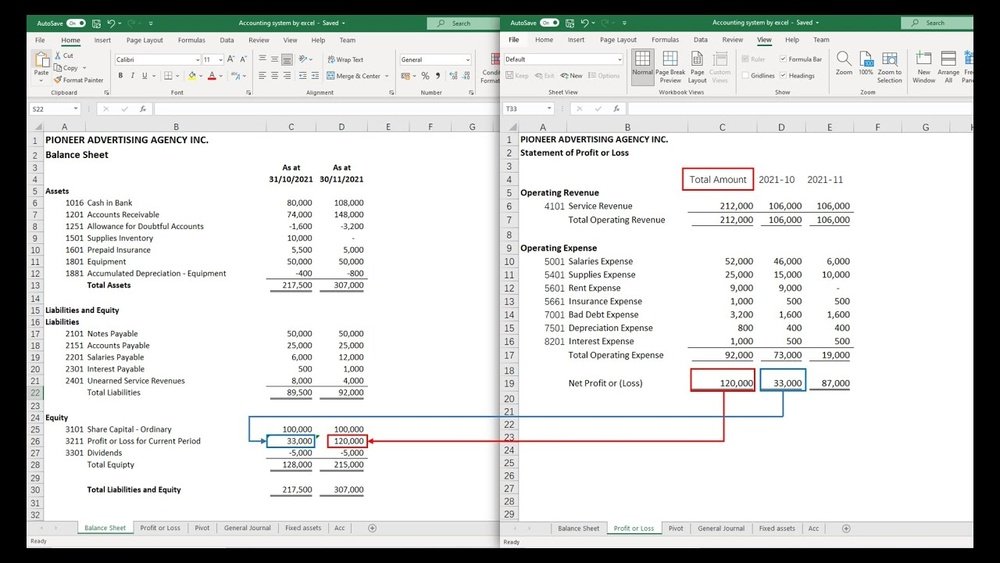
Start by listing all your revenue sources in one column. Below, add all your expenses, such as salaries and rent. Use formulas to subtract total expenses from total revenue. The result shows your net profit or loss. Keep this section simple and clear for easy updates.
Building Balance Sheet
Divide the sheet into two parts: assets and liabilities. List current and fixed assets like cash, inventory, and equipment. Add liabilities such as loans and accounts payable on the right side. Use a formula to calculate owner’s equity. Ensure assets always equal liabilities plus equity.
Preparing Cash Flow Statement
Track cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. Use Excel to sum cash received and cash spent each month. Calculate the net change in cash over the period. This statement helps monitor your business’s liquidity and cash position.

Credit: monday.com
Enhancing With Macros And Vba
Enhancing your accounting software in Excel with Macros and VBA can save time. It helps automate repeated tasks and reduces errors. Even simple automation can improve your workflow a lot.
Macros record your actions, so you don’t repeat them manually. VBA lets you write small programs to control Excel more deeply. These tools make your accounting software smarter and easier to use.
Recording Basic Macros
Start by recording a macro to capture simple tasks. Excel tracks each click and keystroke you make. You can replay the macro to do the task again fast.
For example, record formatting cells or copying data. Save the macro and assign a shortcut key. This saves time on routine steps in your accounting workbook.
Writing Vba Scripts For Automation
VBA lets you write custom code to automate complex tasks. You write simple commands to control Excel’s features. For instance, create scripts to update reports or calculate totals automatically.
VBA also allows you to add logic, like if-then decisions. This makes your software adapt to different situations. Learning basic VBA is easier than it seems and very useful.
Adding Buttons For User Interaction
Add buttons to your Excel sheet to run macros or VBA scripts. Buttons make your software user-friendly and interactive. Users just click a button to perform tasks instantly.
Insert a button from the Developer tab and link it to a macro. Position buttons clearly with labels. This helps users navigate and use your accounting software quickly.
Testing And Debugging
Testing and debugging are crucial steps in building accounting software in Excel. These steps ensure your software works correctly and produces accurate results. Without proper testing, errors can cause wrong calculations and data loss. Debugging helps find and fix these problems fast. This section covers how to check formulas, validate data, and solve common errors.
Checking Formula Accuracy
Start by reviewing all formulas in your Excel sheet. Make sure each formula uses the right cells and functions. Use Excel’s built-in formula auditing tools to trace and check calculations. Test formulas with simple numbers first. Compare results to manual calculations. Fix any mistakes you find. Accurate formulas ensure your accounting data stays correct.
Validating Data Entry
Data entry errors can cause big problems. Set rules for data input using Excel’s Data Validation feature. Limit entries to certain types, like numbers or dates. Use dropdown lists for common options. Check for blank or incorrect fields regularly. Validation keeps data clean and reliable. It helps avoid errors in financial reports.
Troubleshooting Common Errors
Common Excel errors include DIV/0!, REF!, and VALUE!. Each error means something different. DIV/0! shows a division by zero problem. REF! means a broken cell reference. VALUE! signals wrong data types in formulas. Use Excel’s error checking to find errors fast. Fix broken links and correct data types. Track down errors step-by-step to keep your software running smoothly.
Securing And Sharing The Workbook
Securing and sharing your Excel accounting workbook is crucial. It protects your data from accidental changes and unauthorized access. It also helps teams work together without losing important information. You can control who edits and views your workbook easily.
Protecting Worksheets And Cells
Protect worksheets to stop changes in important areas. Lock cells that contain formulas or fixed data. Leave other cells unlocked for data entry. This keeps your work safe from accidental edits. Go to the Review tab and click Protect Sheet. Set what users can or cannot do on the sheet.
Setting Passwords
Add passwords to your workbook for more security. Use strong but easy-to-remember passwords. Passwords stop unauthorized users from opening or changing the file. You can set a password to open or modify the workbook. Save the password safely, as losing it can block access.
Sharing With Multiple Users
Share your workbook for team use without data loss. Use Excel’s built-in sharing feature for multiple users. Enable “Track Changes” to monitor edits from different people. Avoid conflicts by setting clear rules on editing. Save the workbook on cloud storage for easy access by all users.
Maintaining And Updating Software
Maintaining and updating your accounting software in Excel keeps it reliable and efficient. Regular care helps prevent errors and data loss. It also ensures your software meets your changing needs. Simple updates can improve functionality and user experience.
Backing Up Data
Always save a copy of your Excel file before changes. Use cloud storage or external drives for backups. Frequent backups protect your work from accidental loss. Set reminders to back up data regularly. This step guards your financial information and formulas.
Adding New Features
Review your software to find missing features. Add new sheets or formulas to improve tasks. Use Excel tools like macros or pivot tables for automation. Test new features in a copy before applying them. This keeps your software current and useful.
Optimizing Performance
Remove unused sheets and unnecessary formulas to speed up Excel. Use efficient formulas like SUMIFS instead of many SUMs. Limit volatile functions such as NOW or INDIRECT. Keep file size small to avoid slow loading. Regularly check for errors and fix them quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Basic Steps To Create Accounting Software In Excel?
Start by designing a clear layout with income, expenses, and balance sheets. Use formulas like SUM and IF to automate calculations. Incorporate data validation for accuracy. Finally, create charts for visual analysis and secure your workbook with passwords.
Can Excel Handle Complex Accounting Tasks Efficiently?
Excel can manage basic to moderately complex accounting tasks. It supports formulas, pivot tables, and macros. However, very complex or large-scale accounting may require specialized software for better accuracy and scalability.
How Do I Ensure Data Accuracy In Excel Accounting Sheets?
Use data validation to restrict input types. Double-check formulas and use error-checking tools. Regularly audit your data and create backups to avoid accidental loss or mistakes.
Is It Possible To Automate Accounting Processes In Excel?
Yes, automation is possible using formulas, macros, and VBA scripting. These tools help streamline repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and save time in managing accounting data.
Conclusion
Creating accounting software in Excel is simpler than it seems. Start with clear goals and organize your data well. Use formulas to automate calculations and avoid manual errors. Test your sheet often to ensure accuracy. Keep the design clean and easy to follow.
This tool can save time and help track finances effectively. Practice and patience improve your skills. Excel offers a flexible way to manage accounting without extra software. Try building your own and see the benefits firsthand.